GUARD: Guided Unlearning and Retention via Data Attribution for Large Language Models
GUARD: Guided Unlearning and Retention via Data Attribution for Large Language Models
Evelyn Ma, Duo Zhou, Peizhi Niu, Huiting Zhou, Huan Zhang, Olgica Milenkovic, S. Rasoul Etesami
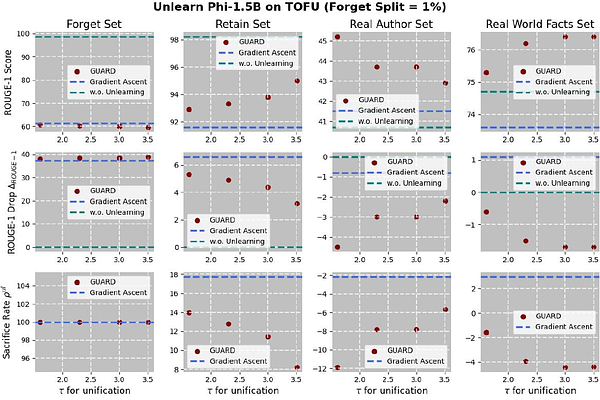
AbstractUnlearning in large language models (LLMs) is becoming increasingly important due to regulatory compliance, copyright protection, and privacy concerns. However, a key challenge in LLM unlearning is unintended forgetting, where the removal of specific data inadvertently impairs the utility of the model and its retention of valuable, desired information. While prior work has primarily focused on architectural innovations, the influence of data-level factors on unlearning performance remains underexplored. As a result, existing methods often suffer from degraded retention when forgetting high-impact data. To address this, we propose GUARD-a novel framework for Guided Unlearning And Retention via Data attribution. At its core, GUARD introduces a lightweight proxy data attribution metric tailored for LLM unlearning, which quantifies the "alignment" between the forget and retain sets while remaining computationally efficient. Building on this, we design a novel unlearning objective that assigns adaptive, nonuniform unlearning weights to samples, inversely proportional to their proxy attribution scores. Through such a reallocation of unlearning power, GUARD mitigates unintended losses in retention. We provide rigorous theoretical guarantees that GUARD significantly enhances retention while maintaining forgetting metrics comparable to prior methods. Extensive experiments on the TOFU benchmark across multiple LLM architectures demonstrate that GUARD substantially improves utility preservation while ensuring effective unlearning. Notably, GUARD reduces utility sacrifice on the Retain Set by up to 194.92% in terms of Truth Ratio when forgetting 10% of the training data.