An Evaluation of Biomolecular Energetics Learned by AlphaFold
An Evaluation of Biomolecular Energetics Learned by AlphaFold
Lyu, N.; Du, S.; Ma, J.; Herschlag, D.
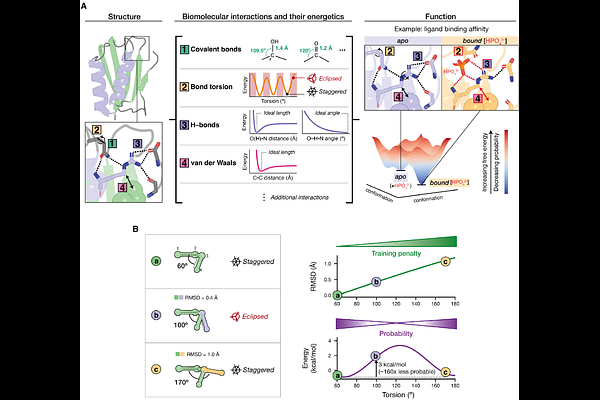
AbstractDeep learning has revolutionized protein structural prediction, with function prediction on the horizon. Because biomolecular properties emerge from atomic-level interactions and their energetics, models that learn physical principles can deliver accurate structural predictions while also providing the foundation for function prediction. We systematically evaluated the state-of-the-art structural prediction models AlphaFold2 and AlphaFold3, interrogating >3.4 million interactions across 3939 structures. These models capture basic energetic principles but show pervasive biases in the conformational preferences of covalent and non-covalent interactions. The conformational biases manifest as mis-assignments for nearly one-third of side-chain interaction partners. Inaccurate energetics are further evidenced by the inability of AlphaFold3 sampling to reproduce experimentally derived ensembles. Our multifaceted, physics-based evaluation identified previously unknown and system-wide limitations in AlphaFold\'s ability to make physically accurate predictions. This information will allow researchers to judiciously apply AlphaFold and guide next-generation models to learn the energetics needed for biomolecular function prediction.