Unveiling mode of action of anthelmintics in Caenorhabditis elegans with SydLab™, an on-a-chip automated and high-content screening system.
Unveiling mode of action of anthelmintics in Caenorhabditis elegans with SydLab™, an on-a-chip automated and high-content screening system.
Duguet, T. B.; Belgrano, C.; Bourgeois, M.; Vernudachi, A.; Mouchiroud, L.; Rufener, L.
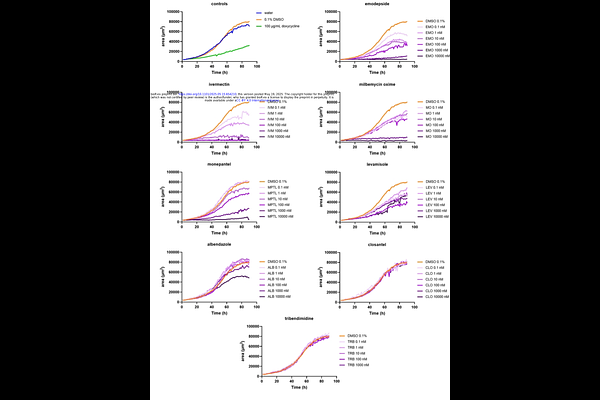
AbstractAnthelmintic resistance in parasitic nematodes presents a growing challenge to animal and human health, driving the need for innovative tools to accelerate drug discovery and mechanistic research. Here, we introduce SydLab, a microfluidic-based, automated phenotypic screening platform that combines continuous imaging, machine vision, and computational analysis for high-content assessment of Caenorhabditis elegans responses to anthelmintics. We systematically evaluated eight anthelmintic compounds spanning major chemical classes--albendazole, ivermectin, milbemycin oxime, emodepside, levamisole, tribendimidine, monepantel, and closantel--across multiple doses. Using wild-type (N2 Bristol) and mitochondrial stress-sensitive (hsp-6::gfp) strains, SydLab captured real-time, dose-dependent phenotypic profiles over 120 hours, measuring developmental growth, reproduction, motility, and morphology. Emodepside, monepantel, and macrocyclic lactones induced severe larval arrest, reduced worm volume, and distinct morphological changes consistent with neuromuscular paralysis. In contrast, albendazole and closantel showed limited effects at tested concentrations. Machine learning-based shape classification revealed drug-specific morphological signatures, including coiling and cuticular damage, offering insights into compound modes of action. Validation with larval development and migration assays confirmed SydLab\'s high sensitivity and reproducibility in detecting subtle phenotypic and strain-specific responses. Our study demonstrates how integrating microfluidics, automated imaging, and computational phenotyping enables precise dissection of complex drug-induced effects in nematodes. SydLab provides a scalable, high-throughput platform for anthelmintic screening and mechanistic studies, offering new avenues for antiparasitic drug discovery and resistance research.