Acute anaphylactic and multiorgan inflammatory effects of Comirnaty in pigs: evidence of spike protein mRNA transfection and paralleling inflammatory cytokine upregulation
Acute anaphylactic and multiorgan inflammatory effects of Comirnaty in pigs: evidence of spike protein mRNA transfection and paralleling inflammatory cytokine upregulation
Dezsi, L.; Kokeny, G.; Szeneasi, G.; Revesz, C.; Meszaros, T.; Barta, B.; Facsko, R.; Szilasi, A.; Bakos, T.; Kozma, G. T.; Dobos, A.; Merkely, B.; Radovits, T.; Szebeni, J.
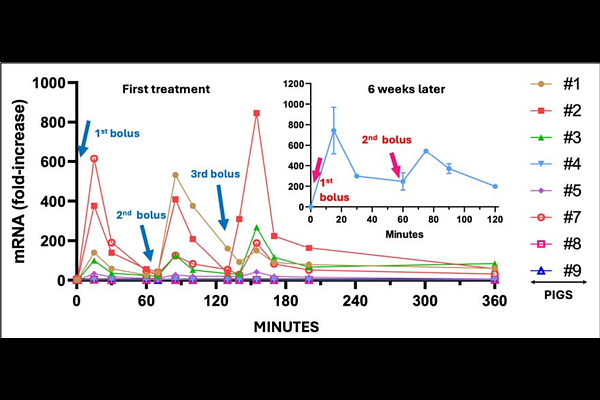
AbstractBackground and Purpose: Rare but serious adverse events (AEs) associated with mRNA-lipid nanoparticle (LNP) COVID-19 vaccines, such as Comirnaty and Spikevax, include acute and chronic inflammatory reactions, the mechanisms of which remain poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate these effects using a porcine model. Experimental Approach: Naive and anti-PEG antibody-sensitized pigs were intravenously injected with Comirnaty. Acute anaphylactic responses were assessed through hemodynamic monitoring, hematological changes, and plasma inflammatory markers. Multiorgan inflammatory effects were evaluated by qPCR detection of spike protein (SP) mRNA uptake and inflammatory cytokine gene expression in seven organs over 6 hours. Histopathology and immunohistochemistry were also performed. Key Results: Severe cardiopulmonary distress developed within minutes of repeated i.v. injections of Comirnaty. qPCR revealed predominant SP mRNA accumulation in liver and PBMCs, with spleen, kidney, lymph nodes, heart, and brain also affected in 40-90% of animals. Repetitive PBMC transfection showed reversible mRNA peaks at 15 minutes, followed by rapid decay. Expression of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1RA, CXCL10, TNF-alpha, CCL2) paralleled mRNA uptake, suggesting a causal relationship. Cytokine profiles varied by organ (e.g. IL-1RA in kidney, CCL2 in PBMCs). Histologic abnormalities and SP immunopositivity were noted in the kidney, heart, and brain. Booster injections replicated PBMC transfection kinetics observed at the first dose. Conclusions and Implications: This porcine model reveals systemic anaphylactic reactivity and multiorgan SP mRNA transfection following i.v. injection of mRNA-LNPs, resulting in organ-specific inflammatory responses. These findings provide mechanistic insights into the rare vaccine-related AEs and may support future efforts to improve the safety of the mRNA-LNP platform technology.