Establishing a standardized genetic toolkit for the radiation-resistant extremophile Deinococcus radiodurans
Establishing a standardized genetic toolkit for the radiation-resistant extremophile Deinococcus radiodurans
Simmons, T. R.; Cordova, A.; Grismore, K. B.; Moline, L. C.; Stankes, A. C.; Johnson, J.; Bok, C.; Contreras, L. M.
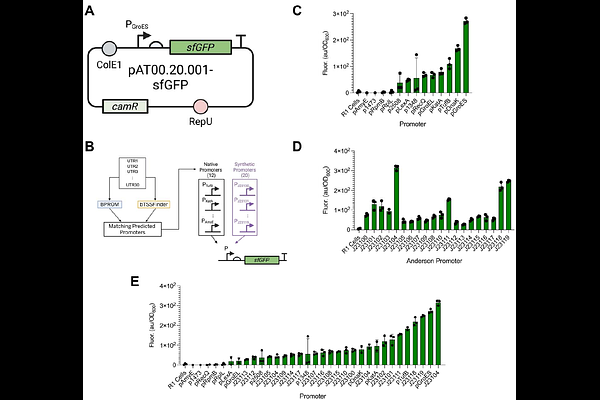
AbstractDeinococcus radiodurans is a highly radiation-resistant extremophile with potential for biomanufacturing and bioremediation in harsh environments, including extraterrestrial settings. However, genetic engineering in this organism has been constrained by limited genetic tools. Here, we establish a comprehensive genetic toolkit for D. radiodurans that enables tunable gene regulation with genome-engineering tools. We have standardized a library of 36 constitutive promoter sequences sourced from the native D. radiodurans genome and from synthetic sources, spanning 45-fold range gene expression in the context of plasmids. We have also identified 136 variants of ribosome binding sites (RBS), variants using a high-throughput screen for precise translational control across a 963-fold range of expression when used in our plasmid-based system. Additionally, we have developed a codon-optimizer script that we leverage to improve the function of four fluorescent proteins in D. radiodurans. Next, we characterized 9 small molecule-inducible promoter systems, and identified four key inducible promoter systems that achieve between 3-fold and 12-fold signal amplification, as well as titratability across induction concentrations in D. radiodurans. To engineer the D. radiodurans genome, we present a novel method for gene integrations, compatible with de novo sequences, up to 3kB in length, doing so with 87% efficiency. Lastly, we repurpose the RNA-directed nuclease, TnpB, as a novel post-transcriptional tool for programmable gene repression analogous to CRISPRi-based systems, and this tool can achieve up to 70% repression of its target. Collectively, this toolkit provides modular, standardized components for both plasmid engineering and chromosomal engineering in D. radiodurans to improve its genetic tractability and to facilitate its deployment.