Sundoli: A necro(w)bot with multi-stiffness joints built using geared mechanical metastructures
Sundoli: A necro(w)bot with multi-stiffness joints built using geared mechanical metastructures
Lee, H.; Mack, J.; Alam, P.
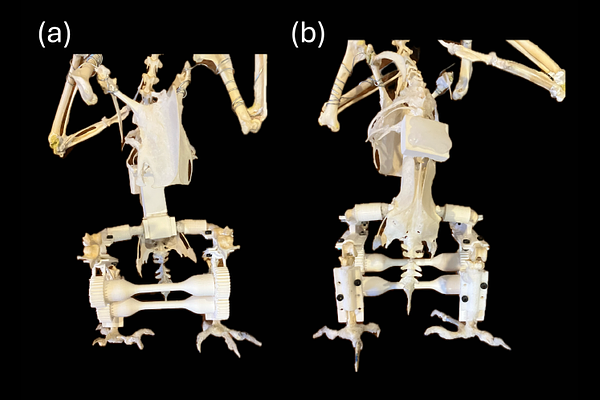
AbstractIn this communication, we design and analyse Sundoli, a necrobot (a bionically engineered robot using decreased animal parts). It is manufactured using a crow endoskeleton, supported and rearticulated by a geared mechanical metastructure to enable controllable passive deformation. The metastructures and bone braces are designed to affix the femur bone to the tibiotarsus, whilst still permitting kinematic movement between the tibiotarsus and the tarsometatarsus of the crow skeleton. The rearticulated hips function as a fulcrum between the upper and lower body parts, whilst concurrently enabling sagittal rotation of the crow skeleton about the hips. Static compression tests, finite element analyses, and in-situ tests conducted using Sundoli shows that the deformation behaviours of metastructures with and without supports are acutely sensitive to the angle of the tarsometatarsus relative to both the ground and the loading direction, highlighting the importance of designing the metastructure holistically and with consideration to the entire skeletal structure. At different loads and angles, the metastructures exhibit variable stiffnesses over their full deformational ranges, demonstrating their effectiveness in protecting the brittle biological bones. Using a metastructure as a mechanism for passive joint rearticulation enables Sundoli an ability to support a payload 8.7 times its body weight without lateral support (an 870\\% payload ratio) and 14 times its body weight with lateral support (a 1400\\% payload ratio). This payload capacity is achievable through the full range of its upper body movement in the sagittal plane throughout the full range of its upper body movement in the sagittal plane.