ASPPs multimerize protein phosphatase 1
ASPPs multimerize protein phosphatase 1
Wei, D. T.; Morrison, K. N.; Beacham, G. M.; Beyrent, E.; Zhang, Y.; Florens, L.; Hollopeter, G.
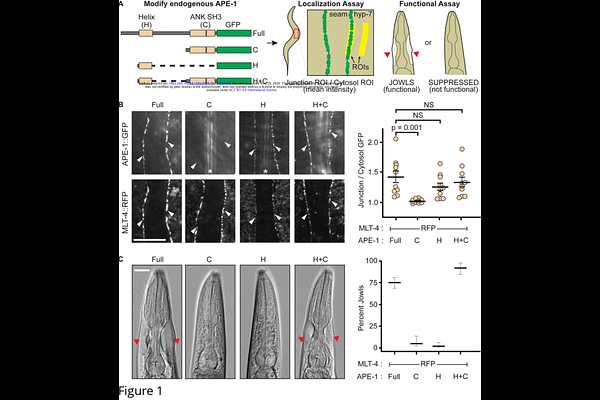
AbstractProtein Phosphatase 1 (PP1) activity is thought to be spatiotemporally defined by hundreds of different regulatory subunits, but their mechanisms of action are largely unknown. The Ankyrin repeat, SH3-domain, and Proline-rich region containing Proteins (ASPPs) bind and localize PP1 to cell-cell junctions. Here, we show ASPPs bind superstoichiometric amounts of PP1. Missense mutations in the ankyrin repeats of ASPPs, that were previously isolated from a forward genetic screen in Caenorhabditis elegans, reduce the stoichiometry of PP1 binding. Forcing PP1 oligomerization restores mutant ASPP function in vivo. We propose that ASPPs multimerize PP1 to establish a concentrated hub of phosphatase activity at cell-cell junctions.