The ALMA Survey of Gas Evolution of PROtoplanetary Disks (AGE-PRO): III. Dust and Gas Disk Properties in the Lupus Star-forming Region
The ALMA Survey of Gas Evolution of PROtoplanetary Disks (AGE-PRO): III. Dust and Gas Disk Properties in the Lupus Star-forming Region
Dingshan Deng, Miguel Vioque, Ilaria Pascucci, Laura M. Pérez, Ke Zhang, Nicolás T. Kurtovic, Leon Trapman, Estephani E. TorresVillanueva, Carolina Agurto-Gangas, John Carpenter, Paola Pinilla, Uma Gorti, Benoît Tabone, Anibal Sierra, Giovanni P. Rosotti, Lucas A. Cieza, Rossella Anania, Camilo González-Ruilova, Michiel R. Hogerheijde, James Miley, Dary A. Ruiz-Rodriguez, Maxime Ruaud, Kamber Schwarz
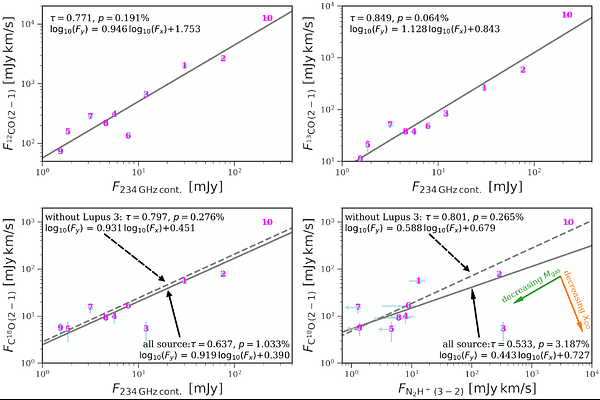
AbstractWe present Band 6 and Band 7 observations of 10 Lupus disks around M3-K6 stars from the ALMA survey of Gas Evolution in PROtoplanetary disks (AGE-PRO) Large Program. In addition to continuum emission in both bands, our Band 6 setup covers the $\mathrm{{}^{12}CO}$, $\mathrm{{}^{13}CO}$ and $\mathrm{C^{18}O}\,J$=2-1 lines, while our Band 7 setup covers the $\mathrm{N_2H^+}\,J$=3-2 line. All of our sources are detected in $\mathrm{{}^{12}CO}$ and $\mathrm{{}^{13}CO}$, 7 out of 10 are detected in $\mathrm{C^{18}O}$, and 3 are detected in $\mathrm{N_2H^+}$. We find strong correlations between the CO isotopologue line fluxes and the continuum flux densities. With the exception of one disk, we also identify a strong correlation between the $\mathrm{C^{18}O}\,J$=2-1 and $\mathrm{N_2H^+}\,J$=3-2 fluxes, indicating similar CO abundances across this sample. For the two sources with well-resolved continuum and $\mathrm{{}^{12}CO}\,J$=2-1 images, we find that their gas-to-dust size ratio is consistent with the median value of $\sim 2$ inferred from a larger sample of Lupus disks. We derive dust disk masses from continuum flux densities. We estimate gas disk masses by comparing $\mathrm{C^{18}O}\,J$=2-1 line fluxes with those predicted by the limited grid of self-consistent disk models of Ruaud et al. (2022). A comparison of these mass estimates with those derived by Trapman et al. (2025), using a combination of CO isotopologue and $\mathrm{N_2H^+}$ line emission, shows that the masses are consistent with each other. Some discrepancies appear for small and faint disks, but they are still within the uncertainties. Both methods find gas disk masses increase with dust disk masses, and gas-to-dust mass ratios are between $10-100$ in the AGE-PRO Lupus sample.