MINDNet: Proximity interactome of the MICOS complex revealing a multifaceted network orchestrating mitochondrial biogenesis
MINDNet: Proximity interactome of the MICOS complex revealing a multifaceted network orchestrating mitochondrial biogenesis
Schaumkessel, Y.; Brocke-Ahmadinejad, N.; Strohm, R.; Mueller, S.; Reichert, A. S.; Kondadi, A. K.
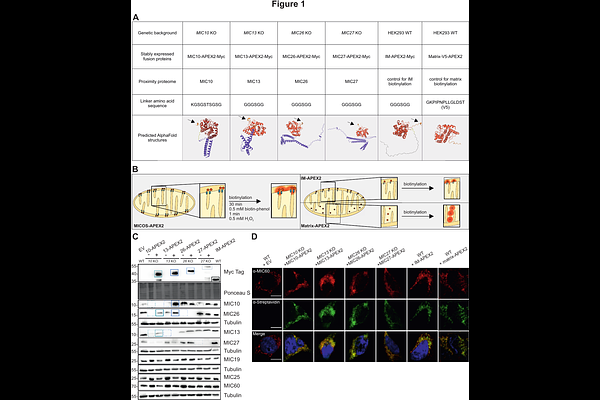
AbstractThe Mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system (MICOS) complex is a multisubunit complex regulating mitochondrial inner membrane (IM) architecture, which is enriched at crista junctions (CJs) and required for cristae membrane dynamics. It modulates various mitochondrial processes including protein and lipid transport and is causally linked to a variety of human diseases. To gain a broad overview of the various pathways modulated by the MICOS complex, we examined its molecular neighbourhood. For this, we employed proximity biotinylation assays using APEX2 fused to four MICOS subunits (MIC10, MIC13, MIC26 and MIC27) in the respective mammalian knockout cells. These four MICOS-APEX2 fusion proteins integrated into the native MICOS complex and properly localised as revealed by electron microscopy combined with DAB staining and STED super-resolution nanoscopy. Here, we identify 119 common and 50 unique proteins, termed MICOS NanoDomain Network (MINDNet) encompassing the versatile proximity proteome of the MIC10/MIC13/MIC26/MIC27 subcomplex playing multifaceted mitochondrial functions. The MINDNet revealed a large number of OXPHOS proteins, protein translocases of the IM and OM, mitochondrial ribosomal proteins and solute carrier family transporters. Using the cues obtained from the proximity interaction studies, we investigated the role of all the MICOS proteins in modulating the function of the OXPHOS complexes. Among all the MICOS proteins, MIC10 and MIC60 consistently regulated the assembly and activity of the OXPHOS complexes. Overall, we propose that the MICOS complex integrates numerous spatial and temporal cues to regulate the dynamic microenvironment, along with IM architecture, which are involved in multiple pathways controlling mitochondrial biogenesis.