Purification of post-transcriptionally modified tRNAs for enhanced cell-free translation systems
Purification of post-transcriptionally modified tRNAs for enhanced cell-free translation systems
Kalb, E.; Alejo, J.; Dias-Fields, L.; Knudson, I.; Davisson, J.; Maldonado, E.; Chattrakun, K.; Lin, S.; Schepartz, A.; Zhang, S.; Blanchard, S.; Engelhart, A. E.; Adamala, K. P.
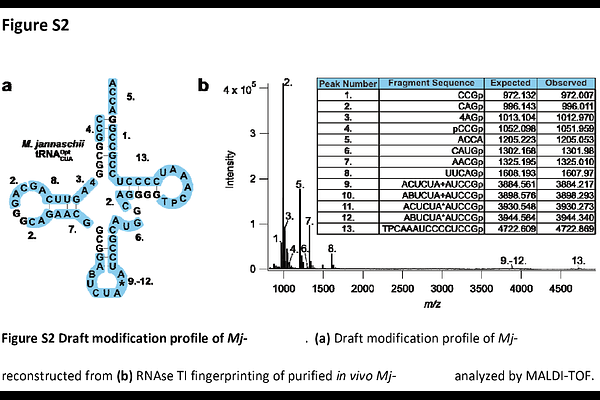
AbstractTransfer RNAs (tRNAs) are utilized by the ribosome to decode the nucleic acid alphabet. tRNA structure, stability, aminoacylation efficiency, and decoding efficacy are governed by their extensive post-transcriptional modifications. In most studies, individual tRNAs are generated using in vitro transcription, which produces tRNAs devoid of these critical site-specific modifications, negatively affecting translation yields and fidelity. To address this, we have developed a purification method which couples tRNA overexpression to DNA hybridization-based purification. Using this approach, we produced native tRNAs from E. coli in high yield and purity while retaining their complement of native post-transcriptional modifications and translational activity. We extend this technique to the purification of Mj-tRNA CUA/Opt and Ma-tRNA CUA/Pyl, tRNAs of critical importance for genetic code expansion. We confirmed that both Mj-tRNA CUA/Opt and Ma-tRNA CUA/Pyl contain native E. coli post-transcriptional modifications and provide the first complete modification profiles of each. Moreover, we found that in vivo-generated Mj-tRNA CUA/Opt significantly outperforms its in vitro-generated counterpart in amber codon suppression in cell-free translation reactions. Finally, we purified an engineered variant of E. coli tRNA CCA/Trp, extending our studies to synthetic tRNAs. We present a flexible method which generates modified tRNAs in high yield and purity, addressing a critical and persistent challenge in RNA biochemistry. This toolkit enables future structural and cell-free studies through scalable access to native and engineered tRNAs, advancing the broader field of translation and synthetic biology.