Improved chromatin QTL mapping with CACTI
Improved chromatin QTL mapping with CACTI
Wang, L.; Liu, X.
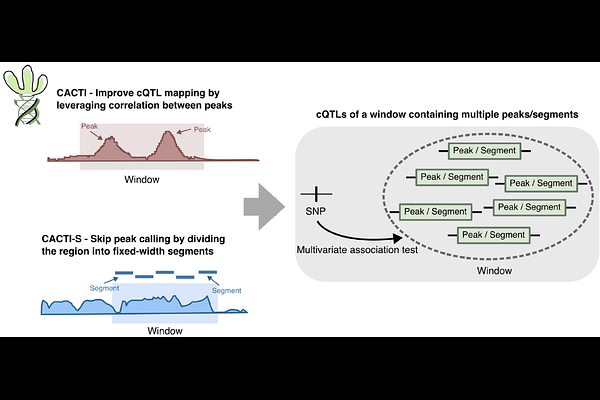
AbstractMapping chromatin quantitative trait loci (cQTLs) is crucial for elucidating the regulatory mechanisms governing gene expression and complex traits. However, current cQTL mapping methods suffer from limited detection power, particularly at existing sample sizes, and are constrained by peak-calling accuracy. To address these limitations, we present CACTI, a novel method that improves cQTL mapping by leveraging correlations between neighboring regulatory elements. Across diverse histone marks (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, H3K27me3 and H3K36me3) and cell types, CACTI identifies 51%-255% more cQTL signals compared to conventional single-peak-based approaches. Using CACTI, we generate a comprehensive cQTL map for the five histone marks across multiple cell types and perform colocalization analyses with GWAS loci from 44 complex traits. CACTI cQTLs colocalize with 6%-47% of GWAS loci, which is on average 15%-424% more than the standard cQTL mapping method across different marks. 24%-75% of colocalized GWAS loci show no colocalization with eQTLs. This underscores CACTI\'s unique ability to uncover regulatory mechanisms that would otherwise remain undetected by eQTL analysis alone, significantly improving the functional interpretation of GWAS findings.