Dissecting ARL15 Function in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Insights from Ex Vivo and In Vitro Synovial Fibroblast Models
Dissecting ARL15 Function in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Insights from Ex Vivo and In Vitro Synovial Fibroblast Models
KASHYAP, S.; PANDEY, A. K.; Paritosh, K.; Kanjilal, M.; Kumar, U.; BK, T.
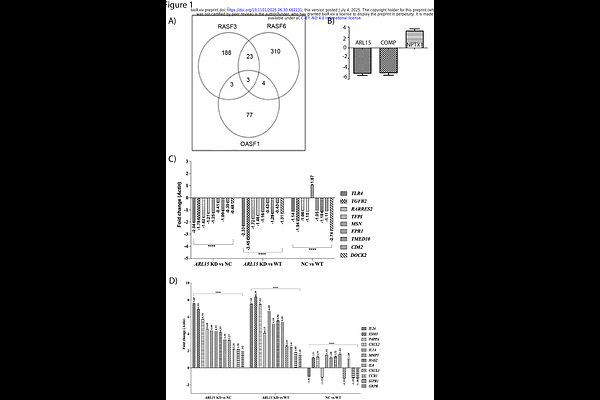
AbstractARL15, coding for a small GTPase was identified as a non-HLA susceptibility gene in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) through a GWAS in a North Indian cohort. Serum adiponectin and ARL15 levels were higher in RA patients with the associated genotype. The present study aimed to delineate the functional role of ARL15 in RA pathobiology using gene knockdown (KD) combined with transcriptomic profiling in both ex-vivo RA synovial fibroblasts (RASF) and in vitro MH7A cell lines. In RASF, ARL15 KD led to the downregulation of COMP-an extracellular matrix stabilizer linked to severe RA-alongside upregulation of adiponectin and IFN response genes such as IFI6 and USP18. Furthermore, upregulation of NPTX1 and MX1, previously associated with disease modulation and treatment response was observed. Downregulation of CTGF, CD248, and PTX3 suggested involvement of ARL15 in inflammation and RA-associated cardiovascular risk. In contrast, ARL15 KD in MH7A cells displayed distinct gene signatures with upregulated cytokines (IL1A, IL8, CXCLs) and downregulated inflammatory regulators (DOCK2, TLR4, TGFB2), reflecting an inflammatory bias distinct from the patient-derived RASF. This divergence highlights the limitations of immortalized cell models in capturing patient heterogeneity and disease complexity. However, the dual-system approach underscores the multifaceted role of ARL15 in regulating connective tissue architecture, inflammation, and immune response. These key findings position ARL15 as a promising therapeutic target, warranting further investigation in RA animal models and genomic medicine. Taken together, this work provides a compelling rationale to pursue ARL15 targeted interventions in RA management.