Purification protocol of hypertrophied hepatic stellate cells for their transcriptomic characterization from CDAHFD mice liver
Purification protocol of hypertrophied hepatic stellate cells for their transcriptomic characterization from CDAHFD mice liver
Heckmann, M.; Djerir, N.-E.-H.; Commere, P.-H.; Fernandes, J.; Sarrabayrouse, G.; Bigey, P.; Escriou, V.; HOFFMANN, C.
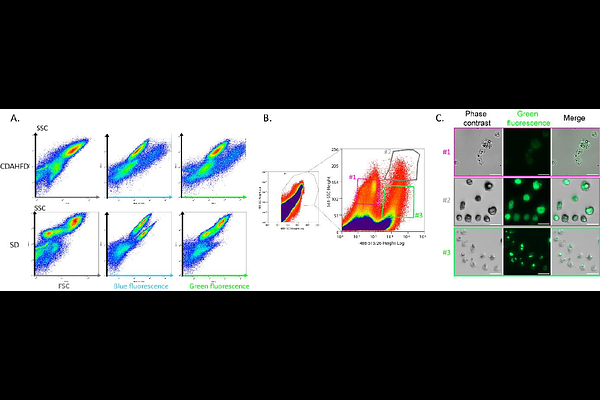
AbstractHepatic stellate cells (HSC) are known for their major role in hepatic fibrosis. Recently, it has been shown that different subpopulations of HSC co-exist during fibrogenesis and play different roles in the establishment of fibrosis. We previously highlighted, in murine model and human biopsies, a specific subpopulation of hypertrophied HSC (hypHSC) which exhibit exacerbated retinoid droplets and were closely associated to collagen fibers. The present study describes the purification protocol of hypHSC developed from a murine model of metabolic liver fibrosis. Liver dissociation followed by density gradient and fluorescence assisted cell sorting allowed us to obtain higlhly pure hypHSC preparations. Then, a transcriptomic analysis (bulk RNAseq) of hypHSCs versus quiescent HSCs purified from healthy mouse liver, was performed. This showed that hypHSCs molecular signature differs from HSC subtypes already described in the literature, with a hybrid profile of both inflammation and matrix remodeling. Our study highlights that a phenotype-to-molecular approach can provide complementary elements to single-cell molecular approaches.