Assessing post-stroke cognition in pre-clinical models: lessons and recommendations from a multi-center study
Assessing post-stroke cognition in pre-clinical models: lessons and recommendations from a multi-center study
Brezzo, G.; Zera, K. A.; Straus, D. E.; Goertz, J. E.; Loppi, S. H.; Crumpacker, R. R.; Frye, J. B.; Becktel, D. A.; Cuartero, M. I.; Culebras, A. G.; Dames, C.; Berchtold, D.; Fowler, J. H.; Meisel, A.; Anrather, J.; Moro, M. A.; Allan, S. M.; Doyle, K.; Buckwalter, M. S.; McColl, B. W.
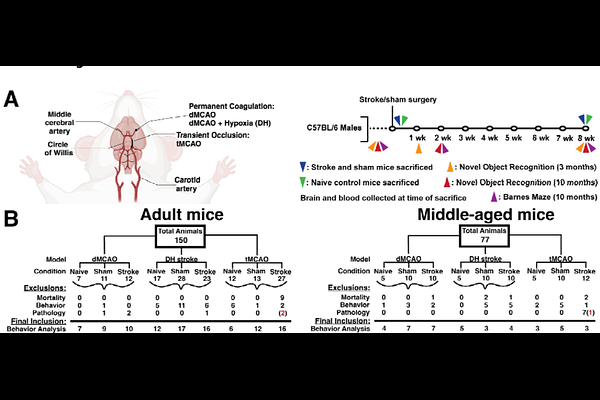
AbstractCognitive decline is a significant long-term consequence of stroke and has no available treatments. To aid in therapy development, we sought to achieve robust detection of cognitive performance after stroke in a multi-site design. Ischemic stroke was induced in adult and middle-aged male C57BL/6J mice utilizing three well-established models: distal middle cerebral artery occlusion (dMCAO), dMCAO with hypoxia and transient MCAO. Cognitive outcomes were assessed via Novel Object Recognition (NOR) and Barnes Maze (BM) tests prior to surgery, and during sub-acute (1-2 weeks) and chronic (8 weeks) phases post-stroke. Histology and immunostaining were used to assess infarct size, tissue damage and neuronal loss, and plasma neurofilament light was quantified. We did not detect a reliable cognitive deficit after stroke using NOR but saw a promising signal from BM (single site tested only). Overall, our study highlights the often-encountered challenges in detecting post-stroke cognitive impairment within the pre-clinical stroke community, as well as a number of complexities in the design and execution of pre-clinical stroke cognition studies, particularly as applied to a multi-site structure. We provide recommendations and suggest important aspects of stroke cognition studies to consider in the future, whether operating as an individual lab or a multi-site group.