JIP4 deficiency causes a novel lysosome storage disease arising from impaired cystine efflux
JIP4 deficiency causes a novel lysosome storage disease arising from impaired cystine efflux
Nassar, L. M.; Shi, x.; Roczniak-Ferguson, A.; Shen, H.; Ferguson, S. M.
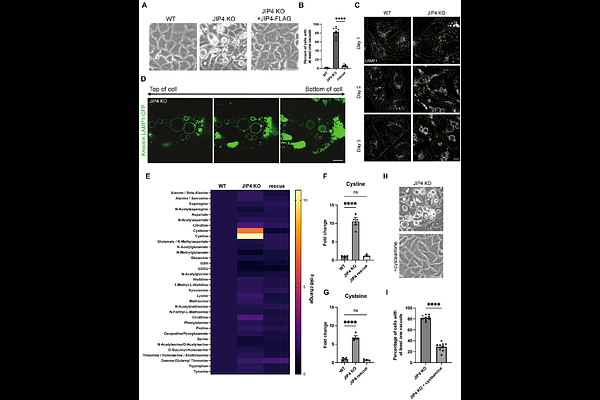
AbstractLysosomes break down macromolecules, clear cellular waste and recycle nutrients such as cystine. We describe a novel mechanism whereby JIP4 regulates lysosomal cystine storage by controlling the abundance of cystinosin (CTNS), the transporter responsible for lysosomal cystine efflux. To this end, JIP4, previously characterized as a motor adaptor and kinase signaling scaffold, suppresses TMEM55B-dependent ubiquitylation of CTNS. Loss of JIP4 reduces CTNS protein levels, leading to lysosomal cystine accumulation and lysosomal storage defects that phenocopy loss of CTNS in both human cells and the renal proximal tubules of JIP4 knockout mice. These phenotypes mirror cystinosis, the lysosomal storage disease caused by CTNS loss-of-function. Our findings thus reveal a fundamental process that controls the efflux of lysosomal cystine and has relevance to understanding human disease arising from JIP4 mutations.