A New Wavelet Scattering Transform-Based Statistic for Cosmological Analysis of Large-Scale Structure
A New Wavelet Scattering Transform-Based Statistic for Cosmological Analysis of Large-Scale Structure
Zhujun Jiang, Xiaolin Luo, Wenying Du, Zhiwei Min, Fenfen Yin, Longlong Feng, Jiacheng Ding, Le Zhang, Xiao-Dong Li
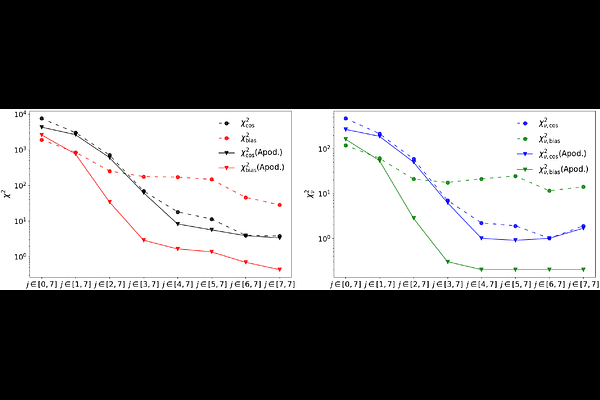
AbstractIn this study, we propose a novel method based on the wavelet scattering transform (WST) to distinguish large-scale structures of the universe across different cosmological models while mitigating tracer bias. By introducing a tailored data preprocessing strategy--particularly a high-density apodization technique--and defining a new statistical measure, the WST $m$-mode ratios, we assess performance using \texttt{CosmicGrowth} N-body simulations across three datasets: WMAP, mWMAP, and Planck. We find that only the WST ratio $R^{\rm wst}$ within the scale range $j \in [3,7]$ achieves a reduced chi-square for cosmological parameters $\chi^2_{\nu, \rm cos} \gg 1$ while maintaining $\chi^2_{\nu, \rm bias} \sim 1$ for tracer bias--a regime unattained by any other statistic. These results highlight $R^{\rm wst}$ as a promising tool for future galaxy surveys, offering strong cosmological sensitivity with effective bias mitigation.