alms1 regulates the immune response and brain ageing in zebrafish
alms1 regulates the immune response and brain ageing in zebrafish
Bea-Mascato, B.; Mendez-Martinez, L.; Costas-Prado, C.; Guerrero-Pena, L.; Suarez-Bregua, P.; Rotllant, J.; Valverde, D.
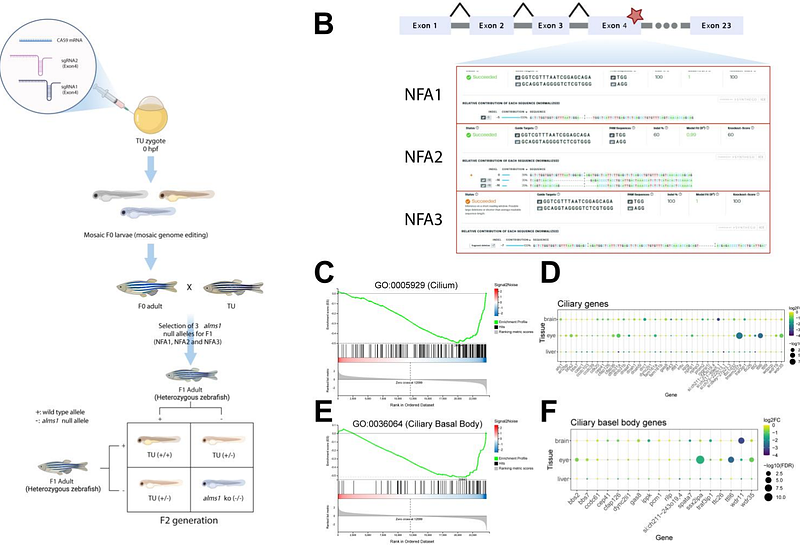
AbstractThe ALMS1 gene plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis through its involvement in primary cilium assembly, cytoskeletal regulation, and signalling pathways such as NOTCH and TGF-{beta}. Pathogenic variants in ALMS1 are associated with Alstrom Syndrome (ALMS), a multi-systemic ciliopathy characterised by neurosensory deficits, metabolic disorders, and multi-organ fibrosis. To better understand the tissue-dependent role of ALMS1, we utilised CRISPR/Cas9 technology to develop a zebrafish model with alms1 depletion. Multi-tissue transcriptomic profiling revealed that alms1 depletion has pleiotropic effects on gene expression, with the brain and eyes displaying the most pronounced transcriptomic alterations, including disrupted ciliary function and immune dysregulation. Inflammatory and innate immune pathways along with glutamatergic synapse-related processes were significantly affected in the brain and eyes but with different gene expression signatures. The analysis further highlights tissue-specific processes, primarily associated with organ dysfunction. Additionally, our findings underscore the role of alms1 in regulating age-associated gene expression profiles in the brain, suggesting a link between ciliary dysfunction and accelerated brain ageing. Comparative analyses with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome iPSC models revealed shared pathways, reinforcing the potential of ciliopathies as models for ageing-related disorders. This study provides novel insights into the tissue-specific functions of alms1 and the molecular mechanisms underlying ALMS, paving the way for the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.