Congenital heart disease missense mutations in the TBX5 DNA-binding domain alter thermal stability and DNA-binding affinity
Congenital heart disease missense mutations in the TBX5 DNA-binding domain alter thermal stability and DNA-binding affinity
Rivera-Madera, A.; Pena-Martinez, E. G.; Messon-Bird, J. L.; Pomales-Matos, D. A.; Echevarria-Bonilla, O. L.; Sanabria-Alberto, L.; Peterson-Peguero, E. A.; Rodriguez-Martinez, J. A.
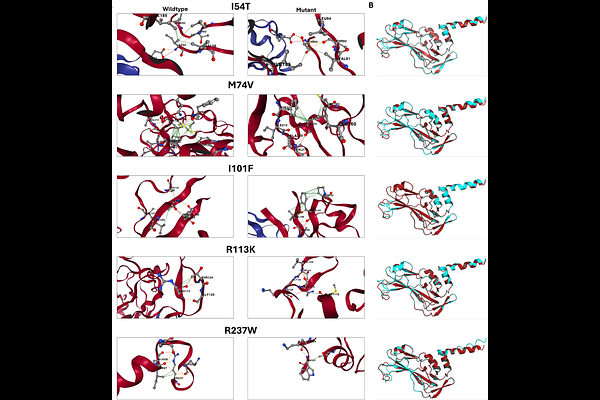
AbstractMissense mutations can alter the biochemical properties of proteins, including stability, structure, and function, potentially contributing to the development of multiple human diseases. Mutations in TBX5, a transcription factor (TF) necessary for heart development, are among the causes of congenital heart diseases (CHD). However, further research on biophysical and biochemical mechanisms is needed to understand how missense mutations in TFs alter their function in regulating gene expression. In this work, we applied in vitro and in silico approaches to understand how five missense mutations in the TBX5 T-box DNA-binding domain (I54T, M74V, I101F, R113K, and R237W) impact protein structure, thermal stability, and DNA-binding affinity to known TBX5 cognate binding sites. Differential Scanning Fluorimetry showed that mutants I54T and M74V decreased thermal stability, whereas I101F and R113K had increased stability. Additionally, DNA-binding affinity decreased for all five missense mutants when evaluated in vitro for known TBX5 genomic binding sites within regulatory elements of Nppa and Camta1 genes. Structural modeling of the TBX5 T-box domain predicted altered protein conformation and stability due to the loss or gain of amino acid residue interactions. Together, our findings provide biophysical and biochemical mechanisms that can be further explored to establish causality betweenTBX5 missense mutations and the development of CHDs.