Blue Stragglers prefer peaceful environments because binaries do the same
Blue Stragglers prefer peaceful environments because binaries do the same
Francesco R. Ferraro, Barbara Lanzoni, Enrico Vesperini, Emanuele Dalessandro, Mario Cadelano, Cristina Pallanca, Giacomo Beccari, Domenico Nardiello, Mattia Libralato, Giampaolo Piotto
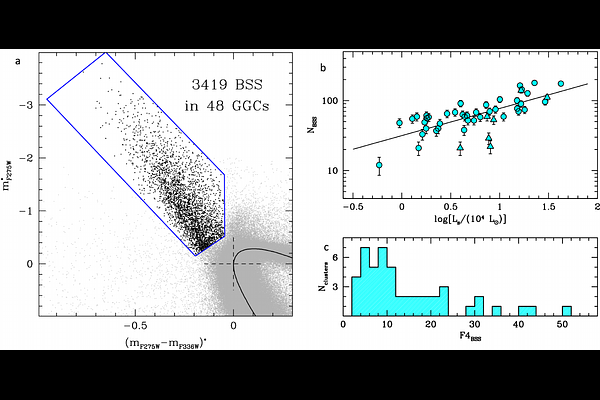
AbstractBlue straggler stars (BSSs) are core hydrogen-burning stars routinely observed in resolved stellar systems. According to the theory of single star evolution they should not exist because, due to their large mass, they should have already evolved to stellar remnants. Hence, they are suspected to be the result of mass-enhancement processes, like mass-transfer activity in binary systems, mergers in binary or higher order systems, or direct stellar collisions, possibly mediated by dynamical interactions. Galactic globular clusters (GGCs) are templates of collisional stellar systems, where frequent gravitational interactions among stars occur on timescales shorter than their age. Thus, in these systems the number of BSSs originated by stellar collisions is expected to increase with the local stellar density and the collision rate. Here we analyse a sample of more than 3000 BSSs homogeneously observed in 48 GGCs with different structures, and we find that the number of BSSs normalized to the sampled luminosity anti-correlates (instead of correlating) with the central density, the collision rate, and the dynamical age of the parent cluster. We also find strikingly similar trends between these environmental properties and the cluster binary fraction, indicating that the latter decreases in high density/high collisional regions. We finally demonstrate that the correlations found between BSSs and the environmental parameters are explained by an underlying dependence of the BSS specific frequency on binary fraction. Once inserted in the context of the current knowledge of the BSS phenomenon, these correlations indicate that low-density regions (possibly because of a higher binary production/survival rate) are the natural habitat of both BSSs and binary systems, and the observed BSSs mostly have a binary-related origin mediated by the environmental conditions.