Grounding Intelligence in Movement
Grounding Intelligence in Movement
Melanie Segado, Felipe Parodi, Jordan K. Matelsky, Michael L. Platt, Eva B. Dyer, Konrad P. Kording
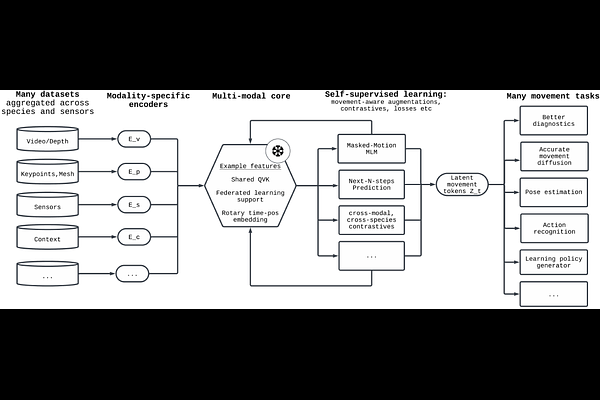
AbstractRecent advances in machine learning have dramatically improved our ability to model language, vision, and other high-dimensional data, yet they continue to struggle with one of the most fundamental aspects of biological systems: movement. Across neuroscience, medicine, robotics, and ethology, movement is essential for interpreting behavior, predicting intent, and enabling interaction. Despite its core significance in our intelligence, movement is often treated as an afterthought rather than as a rich and structured modality in its own right. This reflects a deeper fragmentation in how movement data is collected and modeled, often constrained by task-specific goals and domain-specific assumptions. But movement is not domain-bound. It reflects shared physical constraints, conserved morphological structures, and purposeful dynamics that cut across species and settings. We argue that movement should be treated as a primary modeling target for AI. It is inherently structured and grounded in embodiment and physics. This structure, often allowing for compact, lower-dimensional representations (e.g., pose), makes it more interpretable and computationally tractable to model than raw, high-dimensional sensory inputs. Developing models that can learn from and generalize across diverse movement data will not only advance core capabilities in generative modeling and control, but also create a shared foundation for understanding behavior across biological and artificial systems. Movement is not just an outcome, it is a window into how intelligent systems engage with the world.