Do shifts in honeybee crop microbiota enable ethanol accumulation? A comparative analysis of caged and foraging bees
Do shifts in honeybee crop microbiota enable ethanol accumulation? A comparative analysis of caged and foraging bees
Antoł, W.; Surmacz, B.; Ostap-Chec, M.; Stec, D.; Miler, K.
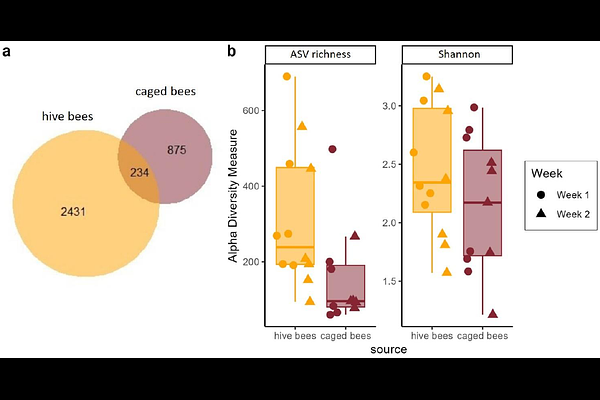
AbstractHoneybees encounter low environmental doses of ethanol, primarily through fermenting nectar, which can have both beneficial and detrimental effects on their functioning. Yet, ethanol traces can also be detected in the crop of caged bees with no access to environmental food sources. This raises the possibility that endogenous ethanol accumulation could occur under restricted conditions, with microbial contributions as a potential mechanism. The crop microbiota, although less diverse than that in other gut segments, plays important roles in food fermentation and pathogen defense. We hypothesized that captivity-induced shifts in crop microbiota may facilitate fermentation, resulting in measurable ethanol. To test this, we compared the crop contents of naturally foraging hive bees and caged bees reared without access to the natural environment. Ethanol levels were low in both groups and did not differ significantly, but non-zero measurements were more frequently observed in caged bees. Microbial community structure differed strongly in - and {beta}-diversity. Caged bees showed reduced abundance of nectar-associated genera (e.g., Apilactobacillus) and an increase in genera that include known ethanol-producing strains, such as Gilliamella and Bifidobacterium. While we did not directly assess metabolic activity, our results suggest that captivity alters microbial communities in ways that may influence ethanol levels. This raises broader questions about how microbe-host interactions modulate host phenotypes under different environmental conditions.