CMB line-of-sight integrators for nearly-isotropic cosmological models
CMB line-of-sight integrators for nearly-isotropic cosmological models
João G. Vicente, Thiago S. Pereira, Cyril Pitrou
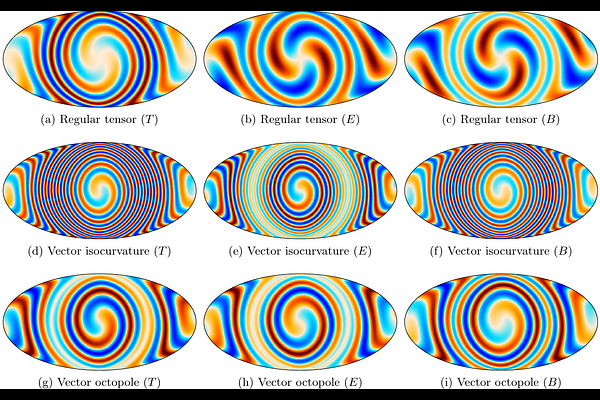
AbstractHomogeneous and nearly-isotropic cosmological models are natural extensions of standard Friedmann cosmologies. Constraining their features is crucial, as any detection of their properties would impact our understanding of inflation and the cosmological principle. Since these models evolve as a set of non-interacting scalar, vector, and tensor modes on top of homogeneous and isotropic spacetimes, their imprints on cosmological observables, particularly the CMB, can be obtained using standard line-of-sight methods. This requires (1) that one resorts on Laplacian eigenmodes on spatially curved spaces and (2) that radial functions for these modes are analytically continued to accommodate complex (i.e., supercurvature) wavenumbers. We introduce two line-of-sight integrators implementing the evolution of the CMB anisotropies in these models: \texttt{AniLoS}, a user-friendly and easy to modify \texttt{Python} package, and \texttt{AniCLASS}, an advanced and efficient extension of the Boltzmann solver \texttt{CLASS}. We discuss possible initial conditions that could generate such fluctuations and provide illustrative examples using our codes. This work offers a pathway for leveraging diverse cosmological datasets to constrain superhorizon anisotropies of the late-time universe.