An aphid-resistant plant metabolite as a candidate aphicide: Insight into the bioactivity and action mode of betulin against aphids
An aphid-resistant plant metabolite as a candidate aphicide: Insight into the bioactivity and action mode of betulin against aphids
Wang, J.; Klakong, M.; Zhu, Q.; Pan, J.; Duan, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Dang, J.; Jing, D.; Zhou, H.
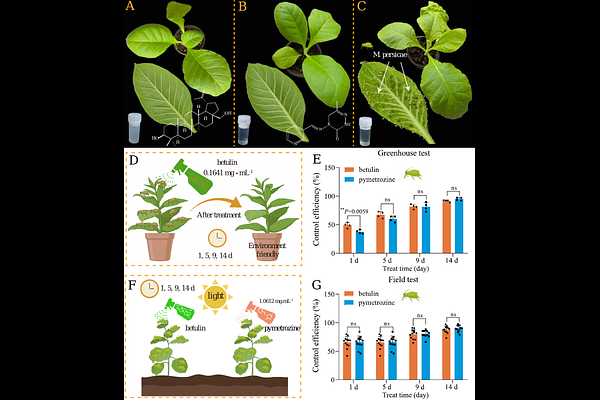
AbstractPest-resistant plants usually utilize secondary metabolites to cope with insect infestation. Betulin, a key bioactive compound in aphid-resistant wild peach, possesses promising applications in crop protection. Here, betulin, in both greenhouse and field experiments, displayed excellent control efficacy against Myzus persicae. RNA-seq, qRT-PCR, and western blotting revealed that betulin significantly inhibited the expression of MpGABR (encoding a GABAA receptor). Besides, RNAi-mediated silencing of MpGABR markedly increased aphid sensitivity to betulin. Furthermore, MST and voltage-clamp assays indicated that betulin bound to MpGABR (Kd = 2.24 {micro}M) and acted as an inhibitor of MpGABR. Molecular docking, mutagenesis and genome editing suggested that THR228 is a critical and highly conserved site in MpGABR that betulin binds to specifically, causing aphid death. Overall, the activity of betulin depends on specific targeting and inhibition of MpGABR. Elucidating the mechanism of action of this peach-derived insecticide may offer a sustainable green strategy for aphid control.