Evaluating the Influence of Disease-Gene Associations in the Significance of Disease Modules through the lens of Network Medicine
Evaluating the Influence of Disease-Gene Associations in the Significance of Disease Modules through the lens of Network Medicine
Gil, A.; Prieto-Santamaria, L.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, A.
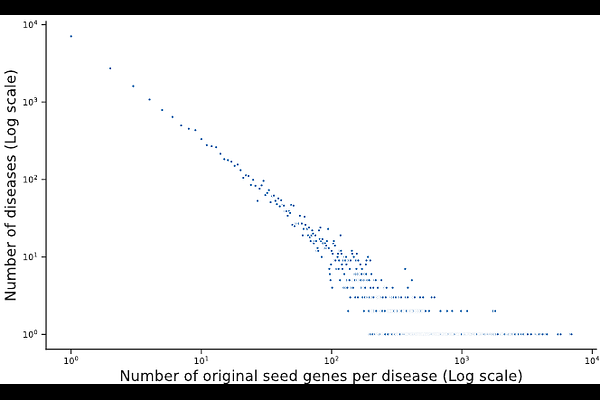
AbstractThe rapid expansion of genomic and biomedical data has paved the way for constructing complex disease networks, offering new insights into disease mechanisms and therapeutic target identification. Central to these networks are disease modules, which are constructed from seed genes that are prioritized based on their relevance to a given disease. Gene prioritization aims to rank genes based on their strength of association with a disease. Resources like DisGeNET, integrated within DISNET knowledge base, assigns a Gene-Disease Association (GDA) score that reflects the confidence in the association between a gene and a disease. This study investigates how both disease module sizes and GDA scores influence the statistical significance of these modules. By characterizing disease modules, filtering the data based on their GDA score thresholds, and analysing the relationship between their size, GDA score, and significance, potential cutoffs for robust module construction are estimated. Our findings suggest that disease modules filtered to include GDA scores above 0.3 and module sizes greater than 10 tend to be significant. These insights provide guidance for optimal gene prioritization and module selection ultimately enhancing strategies for target identification and drug repurposing in network medicine.