Spliformer-v2 predicts multi-tissue RNA splicing and reveals functional genomic links with neurodegenerative diseases
Spliformer-v2 predicts multi-tissue RNA splicing and reveals functional genomic links with neurodegenerative diseases
Tang, X.; Lei, H.; Guo, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, M.
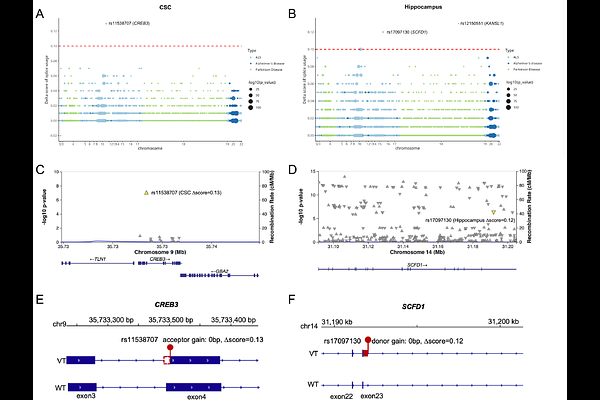
AbstractPrecise regulation of pre-mRNA splicing underpins molecular diversity and is linked to aging and disease. Genetic variants are key drivers of RNA mis-splicing, yet how they induce tissue-specific splicing remains largely unclear. Here, we introduce Spliformer-v2, a deep learning model based on SegmentNT architecture to predict multi-tissue RNA splicing. Spliformer-v2 is trained on paired genome/transcriptome data from 18 human tissues, including 12 central nervous system and 6 peripheral tissues. Spliformer-v2 accurately predicts the effects of heterozygous and homozygous variants on splicing, outperforming existing models (such as SpliceTransformer) across tissues for both regression evaluations (R2: 0.83-0.89 vs 0.10-0.41) and classification evaluations (AUPRC: 0.90-0.95 vs 0.45-0.61). Analysis of ClinVar dataset indicated the link of tissues-specific splicing variants with disease pathogenicity. Analysis of genome-wide association study hits from neurological diseases (such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Alzheimer\'s disease and Parkinson\'s disease) identified tissue-specific splicing variants in genes like CREB3, SCFD1, MAPT and TOMM40, suggesting potential splicing mechanisms in disease. In summary, Spliformer-v2 is a powerful tool for predicting RNA splicing across the most comprehensive set of human brain and spinal cord tissues to date. This advancement enhances our understanding of tissue-specific splicing variants and their roles in neurological and other complex diseases, thereby advancing the discovery of novel drug targets and biomarkers in precision medicine.