Lycopene Suppresses Lung Cancer Progression via PI3K/AKT Pathway Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction: Mechanistic and Safety Insights from Preclinical Models
Lycopene Suppresses Lung Cancer Progression via PI3K/AKT Pathway Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction: Mechanistic and Safety Insights from Preclinical Models
Gu, H.; Pan, C. D.; Xu, Q. D.; Lu, J. D.; Zhao, T. D.; Fu, K. D.; Yan, X. D.; Xu, Y. D.; Ye, J. D.
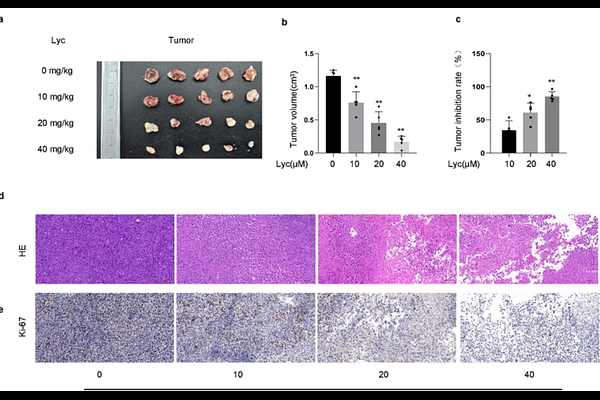
AbstractBackground: Lung cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality, necessitating novel therapeutic strategies with minimal side effects. Lycopene, a natural carotenoid, has shown potential anticancer properties, yet its efficacy and mechanisms in lung cancer models require systematic exploration. Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the antitumor effects of lycopene in both in vivo and in vitro lung cancer models, elucidate its molecular mechanisms, and assess systemic safety. Methods: In vivo, tumor-bearing mice received intratumoral injections of lycopene at varying concentrations (10, 20, 40 mg/kg) to evaluate tumor regression . In vitro, A549 and LLC lung cancer cell lines were treated with lycopene (0-40 M) to assess the ability of clonogenic survival, tumor new cell, cell invasion and promoting apoptosis.Western blot and immunohistochemistry were used to detect related pathways and apoptotic proteins, and target genes were silenced or overexpressed to verify the correctness of the pathways. Systemic toxicity was analyzed through blood biochemical profiling and histopathological examination (HE staining) of major organs at 40 mg/kg. Results: Lycopene significantly reduced tumor volume in mice in a dose-dependent manner (p<0.05). Systemic toxicity assessments revealed no abnormalities in hepatic, renal, or hematological parameters, and organ histology remained unaffected at 40 mg/kg. In vitro, lycopene suppressed colony formation, tumor new cell , cell invasion numbers, and increased apoptosis rates about 60%. Mechanistically, lycopene downregulated phosphorylated PI3K and AKT levels, indicating pathway inhibition. Interference of PI3K gene silencing or overexpression suggests that the PI3K/AKT pathway is the main target for lycopene to produce apoptotic effects. Conclusion: Lycopene exerts potent antitumor effects by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway and promoting apoptosis in lung cancer cells, while demonstrating a favorable safety profile at therapeutic doses. These findings highlight its potential as an adjunctive therapy for lung cancer management.