Benchmarking Spectral Library and Database Search Approaches for Metaproteomics Using a Ground-Truth Microbiome Dataset
Benchmarking Spectral Library and Database Search Approaches for Metaproteomics Using a Ground-Truth Microbiome Dataset
Rajczewski, A. T.; Mehta, S.; Wagner, R.; Gabriel, W.; Johnson, J.; Do, K.; Vintila, S.; Wilhelm, M.; Kleiner, M.; Searle, B. C.; Griffin, T.; Jagtap, P.
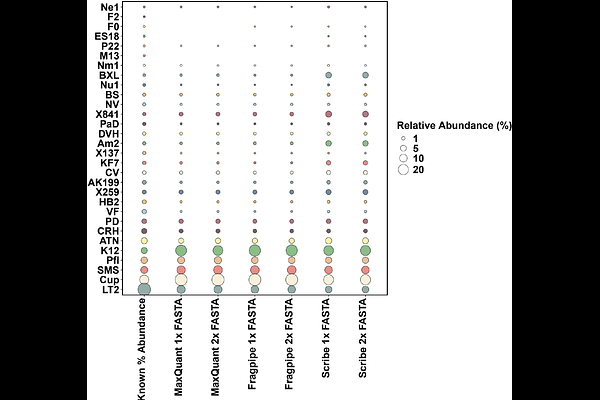
AbstractMass spectrometry-based metaproteomics, the identification and quantification of thousands of proteins expressed by complex microbial communities, has become pivotal for unraveling functional interactions within microbiomes. However, metaproteomics data analysis encounters many challenges, including the search of tandem mass spectra against a protein sequence database using proteomics database search algorithms. We used a ground-truth dataset to assess a spectral library searching method against established database searching approaches. Mass spectrometry data collected by data-dependent acquisition (DDA-MS) was analyzed using database searching approaches (MaxQuant and FragPipe), as well as using Scribe with Prosit predicted spectral libraries. We used FASTA databases that included protein sequences from microbial species present in the ground-truth dataset along with background protein sequences, to estimate error rates and assess the effects on detection, peptide-spectral match quality, and quantification. Using the Scribe search engine resulted in more proteins detected at a 1% false discovery rate (FDR) compared to MaxQuant or FragPipe, while FragPipe detected more peptides verified by PepQuery. Scribe was able to detect more low-abundance proteins in the microbiome dataset and was more accurate in quantifying the microbial community composition. This research provides insights and guidance for metaproteomics researchers aiming to optimize results in their analysis of DDA-MS data.