Assessing Large Language Model Alignment Towards Radio-logical Myths and Misconceptions
Assessing Large Language Model Alignment Towards Radio-logical Myths and Misconceptions
West, C.; Wang, Y.
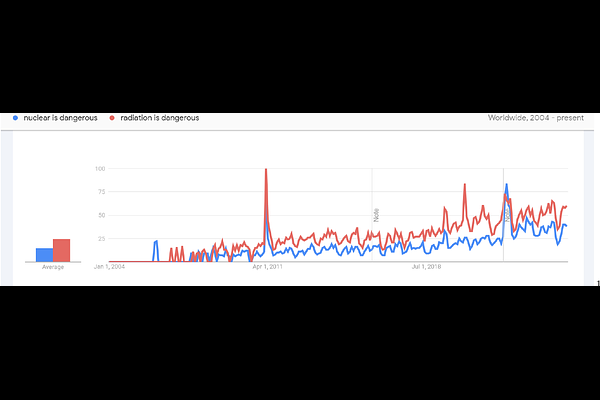
AbstractHumans are susceptible to believing in or espousing myths and misconceptions in the radiological field. Since the advent of large language models (LLMs)-with applications such as ChatGPT processing over one billion queries per day, and Gemini now integrated into Google\'s search engine-these models have steadily evolved into a major source of information for vast audiences. The aim of our study was to assess whether large language models, which are primarily trained on human-generated data, are susceptible to the same underlying sentiments and biases with regards to radiological topics. Furthermore, we assess the use of large language models in both detecting and analyzing trends in the circulation of radiological myths and misconceptions in online communities. Finally, we evaluate the use of large language models as supportive tools for improving communication on these controversial topics.